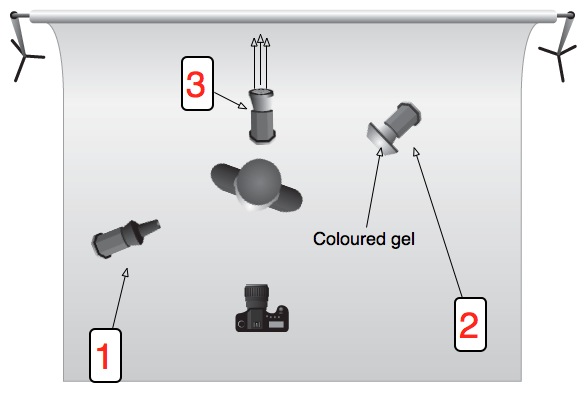
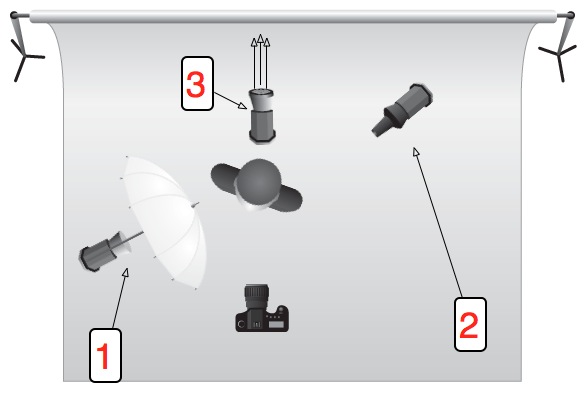
When I first started to use Lightroom to post-process my images, I described its non-destructive capability as being able to go back to your teacher and ask for a new sheet of drawing paper when you'd messed up your finger-painting by adding a few too many red splodges. When you're editing your work first time around, this is marvellous, wondrous, and often absolutely heaven-sent. But what about second time around? Third time around? A few years down the road? You change, you learn more, fashions change, and suites are upgraded. You can still go back, dig out that original Raw file, and edit it all over again. Gareth is here to tell precisely why you should be doing this.
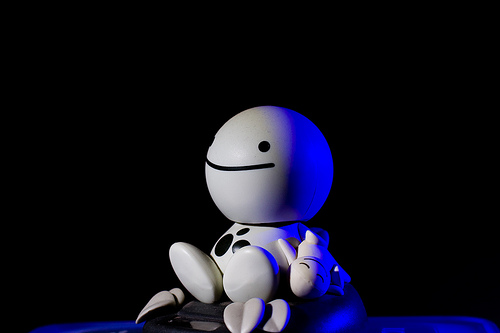
Today, we're going to look at some photos with horrible processing and make fun of them. You might think that is harsh, cruel, or even downright bad form, but I don't care: I'm here to kick the ever-loving shingles out of these images because they're bad. Compositionally and conceptually, they're fine, but the processing on them is horrible. So we're going to tear them apart (semi-constructively) and tell you what's bad about them, and how bad or unnecessary processing can lead to an inferior portfolio, and what you can do to improve your existing work without leaving your computer.

Easy on the clarity slider, buddy – I can only imagine this chap thought 'Maybe if I keep hitting "sharpen", the image will get better and better every single time! I've seen Manny Librodo's stuff – everyone loves that guy. Let's copy it!'
Add to that the weird yellow glow which I can only imagine is coming from a nearby burning Lancaster Bomber and you have an introspective moment ruined by gaudy, overblown highlights and a shirt that STANDS OUT like a neon, strobe-lit fifty foot long thumb. Ugh.

Someone get some ice on that guy's cheek, it appears to be approaching 1,000 degrees Celsius. Not only that, but I'm pretty sure that's a wig: nobody's hair is THAT shiny.

Now this is an absolute cracker. What better way to draw attention away from the background than to put a massive, gaudy vignette around your image? I mean he might as well have put a large, red arrow pointing at the subject, accompanied by the words 'HERE! THE THING YOU SHOULD BE LOOKING AT IS THE DUDE IN THE MIDDLE. OK? GLAD I COULD HELP, DUDE.'
As for the headshot, I see the Germans took down another one of our brave pilots. Better move away from that burning wreckage, my friend – it looks like you're within about a metre of it.
The Not-at-all-obvious Reveal
These photos all have something in common: they're all my photos. 'Crikey O'Reilly of the First Degree!' I hear you exclaim, as your monocle pings out and shoots across the room, ricocheting off your cat, Mr Plot Twist, and sends him screeching and careering out of the room.
We all know it's very easy to allow your online portfolio to go stale: we diligently replace our old images with new, better work, ensuring only a representative and varied handful of our best work is on display at all times. Don't we? Admittedly sometimes we forget, and we all probably need to update, replace and trim the deadwood more often than we do. However, there is another way a portfolio can go stale, something that is much harder to detect: I'm talking about our processing.
My process of keeping my online portfolio up to date usually goes as follows: look over recent shoots and pick some of my absolute favourite images, look at my existing online work, hold a sort of faux television talent show where I print out all the photos, consider each one intently, and then pause for a ludicrously long time–giving everyone involved the collywobbles, or just sending them catatonic with boredom–before announcing who's made the cut and is still in with an opportunity of landing themselves a Christmas number one and first album deal that everyone will promptly ignore after the next series. Oh, sorry, no, just a place on my website. But anyway, the point is, I clean out the deadwood and ensure that only my best work is on display... except there's something I've missed.
With every portfolio update, there are always a couple of images that never get cut. This usually is either down to them having a particularly interesting quality or because they are notable in some other way, such as being a portrait of someone well known (or well known in the videogame world, in my case). The problem is, these images tend to evade scrutiny with each portfolio update. Well it hit me the other day when looking at some of my images that survive the cut every time, just how rough the processing was and how much I had learned since I'd first taken them, processed them, and uploaded them with a glowing sense of pride to my website.
I decided to pull the original files off my backup external hard drive (you are all backing up your images, right?) and reprocess some from scratch. Not only did they look better, thanks to a more careful post-processing approach than my previous, ham-fisted attempts, the reprocessed images actually helped my portfolio look stronger as a whole, as these new images now fitted into to the overall aesthetic a lot better. What I ended up with was a more consistent look which reflects my current style, instead of a fairly consistent style punctuated by nasty little poorly processed shots.
It's a really great, uplifting thing to do: I was happy with what I had captured in these images but shocked at how I had treated them in post. In addition, it allowed me to reflect on what lessons I had learned from my days as a naive, wet-behind-the-ears but terribly enthusiastic post-processor to where I am today.
One of my biggest lessons? You don't need to over-process everything. Sometimes a shot benefits from an aggressive filter. Sometimes a vignette is appropriate: it depends on your customer, the target audience, and the theme.
For example, although I reprocessed a couple of the photos of game designer and artist Keita Takahashi, I retained the aggressive processing, because the images are intended to reflect Takahashi's wild and bizarre imagination. Seeing as the background is a mural painted by Takahashi himself, I wanted the images to feel like we were inside his imagination.

More often than not, however, filtering and gaudy effects are unnecessary and often detract from the final image. Keep your eye on what's interesting in the original image and draw out that; if there's nothing of interest there, then it's probably not the photo for your portfolio.
Another lesson learned was the importance of good cropping, an understanding and respect of the power of composition and how it can can draw out a lot more from an image than a gaudy filter.

I looked at the image of Peter Molyneux sat at a table with the counters properly for the first time in a long time and wanted to crawl into a very tiny space, never to emerge, feeding on moss and small insects that were unlucky enough to scuttle into my awful, fauxtographic gobhole. What was I thinking adding that horrendous vignette?! If I wanted to draw attention to the subject, a good crop would do a significantly better job than a vignette on a whiteboard.
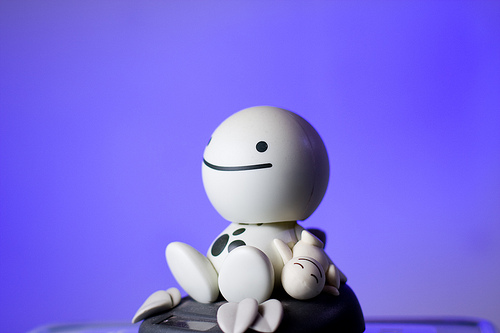
And just for completeness, here are the re-edited versions of the other two originals:


It will hurt and it will force you to critically tear your own work apart but it's a bit like doing the vacuuming: the longer you leave it, the worse it will get, but you'll feel so much better afterwards.
The illustration is by the talented James of Sweet Meats Illusttration.