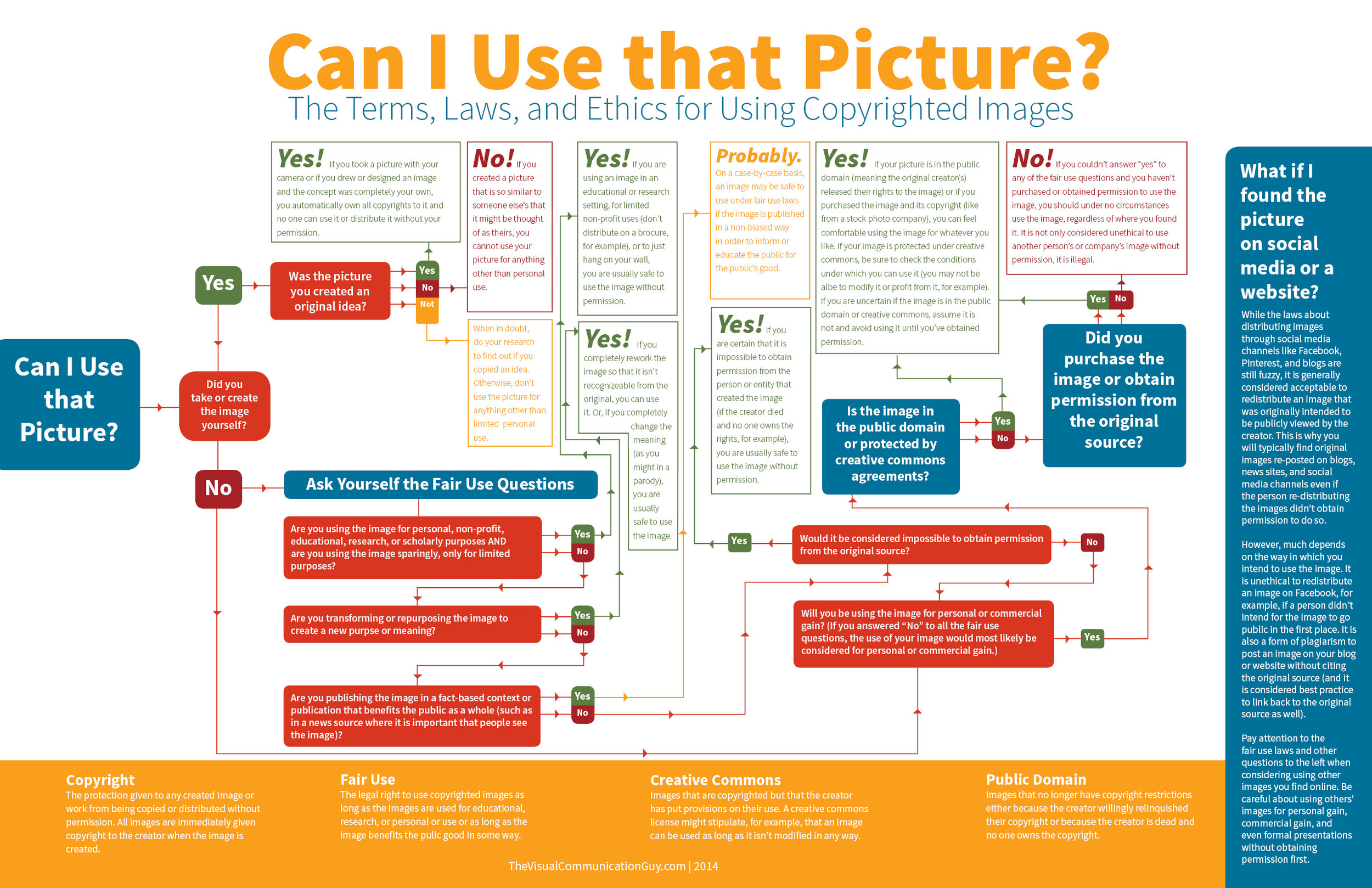
I was having a fairly good morning, until I took my lunchtime peruse of Feedly to see if anything interesting or exciting had dropped into it. Apart from a new post by my favourite film critic, nothing was outstanding until I reached Lifehacker. The Lifehacker team has just posted a link to a visual media usage rights flowchart created by The Visual Communication Guy. Excellent! Ignorance is no excuse when it comes to image theft and unauthorised use and reproduction of photos. While we're all perfectly aware that when you place something on Facebook, Flickr, or your personal version of Frankie's Funky Photos, there's a real chance that someone will try to use it improperly, the more that we can educate people about the right way to do things, the better. This one, however, was not quite so excellent.
You'll find the original here and the Lifehacker article here.
Apart from the fact that it's far too dense and word-heavy, it contains at least one humongous, glaring, verging on the unforgiveable fault for something that purports to advise on usage rights. Take a look and tell me if you can see it. (And tell me how many others you can see. There are plenty.)
Found it?
If you haven't, because it's a horrid thing to read, here it is:
While the laws about distributing images through social media channels like Facebook, Pinterest, and blogs are still fuzzy, it is generally considered acceptable to redistribute an image that was intended to be viewed publicly by the creator. This is why you will typically find original images re-posted on blogs, news sites, and social media channels even if the person re-distributing the images didn't receive permission to do so.
No, no, no, no, no, no. And for good meaure I'll say it again. No.
Images that are shared on social media aren't free for redistribution unless the creator has expressly said so. I put my images on Flickr and use them here on Photocritic and put them on my personal website to display them, to illustrate concepts, to tell stories. I do not put them on the Intergoogles so that anyone else can make use of them. And you should never assume that anyone else does, either.
The law regarding this is hardly fuzzy about the situation, either. There's been at least one monumental court case that supports this opinion, when photographer Daniel Morel sued AFP and Getty Images after they redistributed his images from the Haitian earthquake, which he'd shared via Twitter, without his permission.
Copyright exists from the moment that someone creates something, whether it's a photograph, a tune, a poem, or a piece of prose. It doesn't matter how a creator wishes to share her or his creation with the world, unless she or he has definitely signed away the rights to it, the rights remain theirs.

To be fair to the Visual Communications Guy, he does state 'My rule above all else? Ask permission to use all images. If in doubt, don’t use the image!' in the post that accompanies the flowchart, but that's not really good enough. It's the flowchart that people are going to share and see, not the article. When incorrect information such as this gains traction, we all suffer. Suddenly what's not right becomes commonly accepted. Or people who were doing their best to not be ignorant are in the wrong when they thought they were doing right.
So I'll say the mantra and everyone can repeat it after me: 'Just because I found it on the Internet, it doesn't mean it's free to use.'